
Colles smith fracture full#
The trauma of a fracture is usually associated with local swelling and so a full cast must be avoided initially, as the swelling may impede the circulation and can produce ischaemic contractures.The treatment of a fracture involves immobilisation and the general principle is that the joint above and the joint below the fracture should both be immobilised.This is more likely to be required if there is both a fracture and a dislocation. If it is not possible to achieve satisfactory reduction of a fracture, with or without dislocation, then operative treatment is required.The method of reduction varies depending on the fracture.This should be performed by healthcare professionals trained in the technique, not necessarily anaesthetists.
Intravenous regional anaesthesia (Bier's block) should be considered when reducing dorsally displaced distal radius fractures in adults (16 or over) in the emergency department.A novel technique, which avoids the risks of local anaesthetic leakage or excess sedation, is the proximal periosteal block.They concluded that there was inadequate evidence of robust quality to make an adequate comparison of the various techniques. However, haematoma block is quicker, easier to perform and less intensive on resources. All methods were effective but regional block was probably more effective than haematoma block. It also looked at associated physical techniques and drug adjuncts used for the management of distal radial fractures in adults. A Cochrane review examined the main methods of anaesthesia: haematoma block, intravenous regional anaesthesia (IVRA), regional nerve blocks, conscious sedation (also known as 'moderate sedation/analgesia') and general anaesthesia.

It is also necessary to wait until at least four hours after anything was taken by mouth.
Colles smith fracture skin#
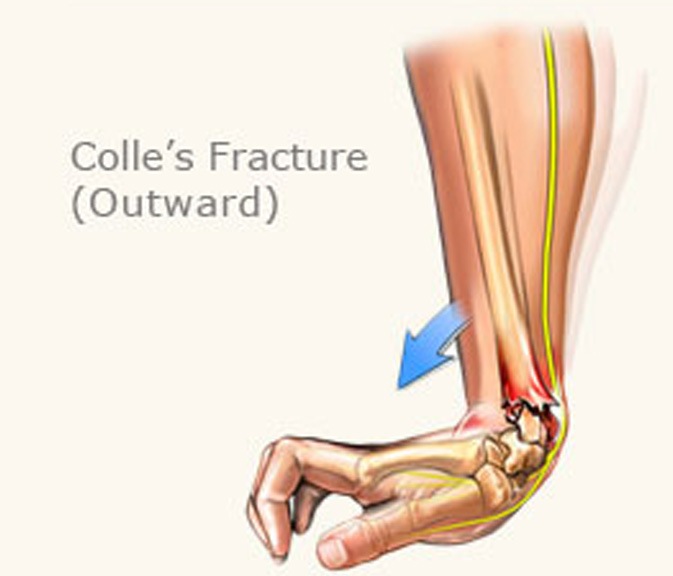
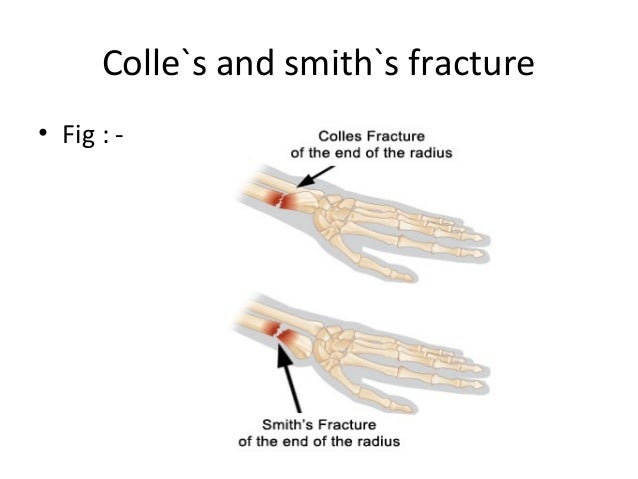
Assess for deformity and examine for any skin defects that might lead to a diagnosis of a compound fracture.Assess Airway, Breathing and Circulation and manage as necessary.Wrist fractures treatment and management Does the patient feel that it is unstable?.Was there a sound or a feeling of something breaking on impact?.What was the mechanism of injury? Note the degree of trauma, as fracture with a mild force suggests osteoporosis.They also become more common with advancing age, partly because advancing age is related to an increased risk of falls and partly because of osteoporosis.They are more common in children and in young adults, especially those involved in risk-taking activities.Fractures of the wrist are common, representing about a quarter of all fractures of limbs.The trauma is often bilateral, with proximal lesions (elbow) very often associated with contusion or compression of the median nerve. High-energy injuries to the wrist may involve complex fractures of the distal radius, radiocarpal dislocations, perilunate dislocations, and other intracarpal dislocations, depending on the energy of the injury and the position of the wrist at the time of impact. Greenstick fracture (confined to children).Chauffeur's fracture (fracture of the radial styloid).Barton's fracture (fracture dislocation of the radiocarpal joint).Smith's fracture (distal radius with volar displacement of fragments).Colles' fracture (distal radius with dorsal displacement of fragments).If the bone is fractured and the overlying skin is broken this is a compound fracture and must be treated as such. Classification of wrist fractures Īs with fractures elsewhere in the body, wrist fractures can be:įor a fracture to be compound, the bone does not have to be protruding through the skin. See also the separate article on Carpal Fractures and Dislocations.
Wrist fractures in the elderly are associated with deformity and significant and prolonged/permanent loss of dependence, especially in frail patients. Accurate diagnosis and correct treatment help to prevent long-term loss of function. The eight carpal bones are injured less frequently. Three quarters of wrist injuries are fractures of the distal radius and ulna.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
